函数
说明
- 函数的定义:def + 名字 + (参数起名字) :return 返回值
return后面为一个函数的返回值,可以有也可以没有。- 之前提过函数,他并不是数学中所谓的函数
- 函数就是有一些功能,这块功能被打包了一块
py
# 定义函数:计算两个数的和
def add(a, b):
return a + b
"""
函数说明:计算两数之和
参数:
a - 第一个数
b - 第二个数
返回值:a + b
"""
result = add(5, 3)# 调用函数
print(f"两数之和为:{result}") # 输出:两数之和为:8
#------------------------------------------------------------
# 这样的写法把print打包进去了
def add(a,b):
result = a + b
print(f"两数之和为:{result}")
add(5,3) #调用函数,输出:两数之和为:8- 可变参数:
- *args:接收任意数量的位置参数(转为元组)。
- **kwargs:接收任意数量的关键字参数(转为字典)。
py
def show_info(name, age, *hobbies, **kwargs):
print(f"姓名:{name},年龄:{age}")
print(f"爱好:{hobbies}")
print(f"其他信息:{kwargs}")
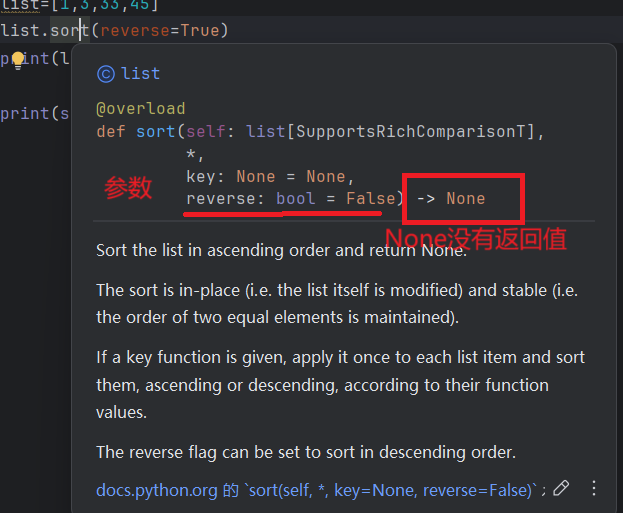
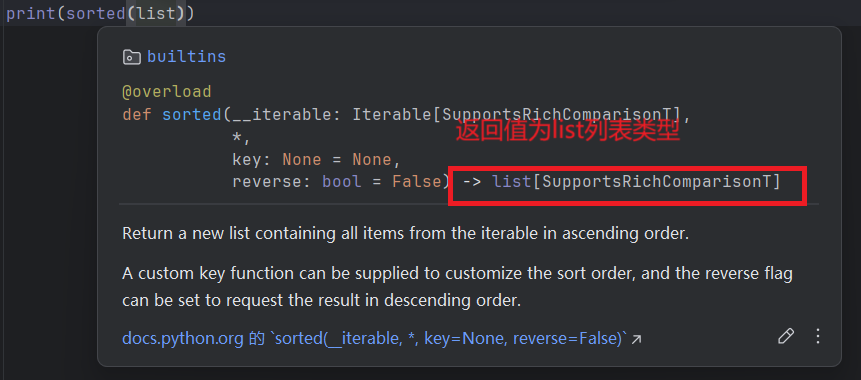
show_info("华子", 18, "睡觉","运动", city="美国边缘小岛", job="无业游民")查看函数的参数类型和返回值
- 鼠标拖动到函数名,停留几秒后就会有提示
模块
说明
- 模块可以理解为一个大的功能代码,被打包在一个py文件里
- pip第三方库里面有很多别人已经写好的代码功能,这也是模块
- 模块的导入方法:
- import 模块名:导入整个模块(如
import turtle)。 - from 模块 import 函数 / 变量:导入特定内容(如
from math import sqrt)。 - import 模块 as 别名:为模块取别名(如
import turtle as t)。
py
#示例:利用海龟库画一个圆
import turtle #导入模块
turtle.setup(800,400) #初始化窗口长800,宽400
turtle.circle(20,360) # 半径20,弧度360
turtle.done() # 程序运行完保持窗口不自动关闭
#----------------------------------
from math import sqrt #导入math库里面的sprt开方函数
number = 16
result = sqrt(number) # 直接使用 sqrt()
print(f"16 的平方根是 {result}") # 输出: 4.0
#----------------------------------
import turtle as t#导入模块,起个名字t
t.setup(800,400) #初始化窗口长800,宽400
t.circle(20,360) # 半径20,弧度360
t.done() # 程序运行完保持窗口不自动关闭from improt和 import导入区别
- import math:这种方式是直接导入 math 模块。当你要使用其中的类或者函数时,需要加上模块名作为前缀,例如math.sqrt(),math.pow()。
- from math import *:这是从 math 模块里导入所有的公共名称,像类、函数、常量等。导入之后,使用这些名称就无需添加模块前缀,直接写 pow(),sqrt()就行
py
import math
a = math.sqrt(16) # 调用函数需要加math.
print(a) #输出是4.0py
from math import sqrt # 只导入了一个函数
a = sqrt(16) # 直接调用
print(a) # 4.0有关 pip
- pip是py的第三方库,里面有非常丰富的库,免费开源提供下载。也就是模块,事先写好功能。这也是py好用的原因。
- pip库官方地址:https://pypi.org/project/pip/
- 示例:下载一个
pygame库
- 通过终端下载,在黑白窗口敲命令
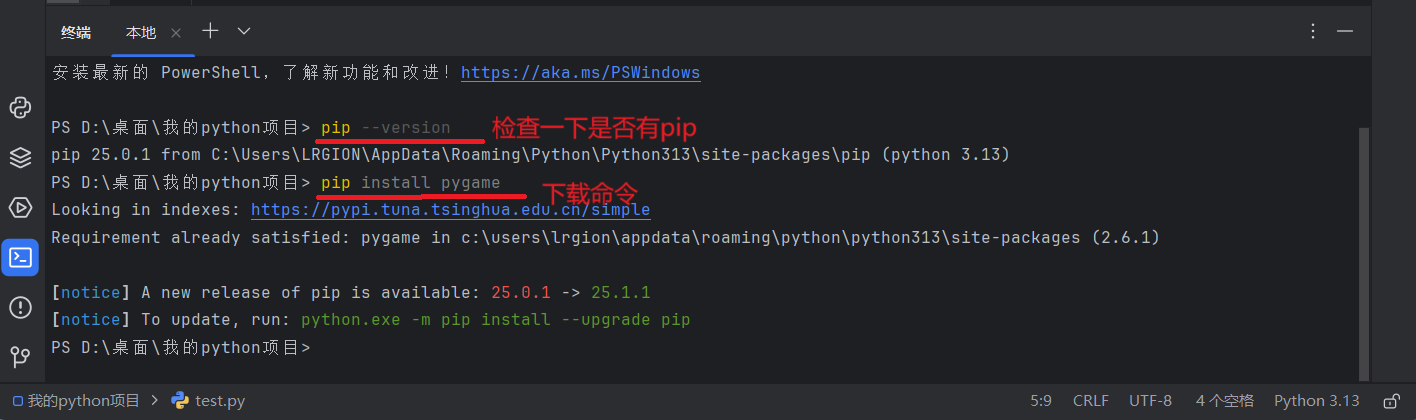
- 如果终端显示找不到可执行命令,可能是没有配置pip的环境变量,再一个就是没有安装pip。我在前面的(环境搭建与IDE)里有讲过环境变量的配置
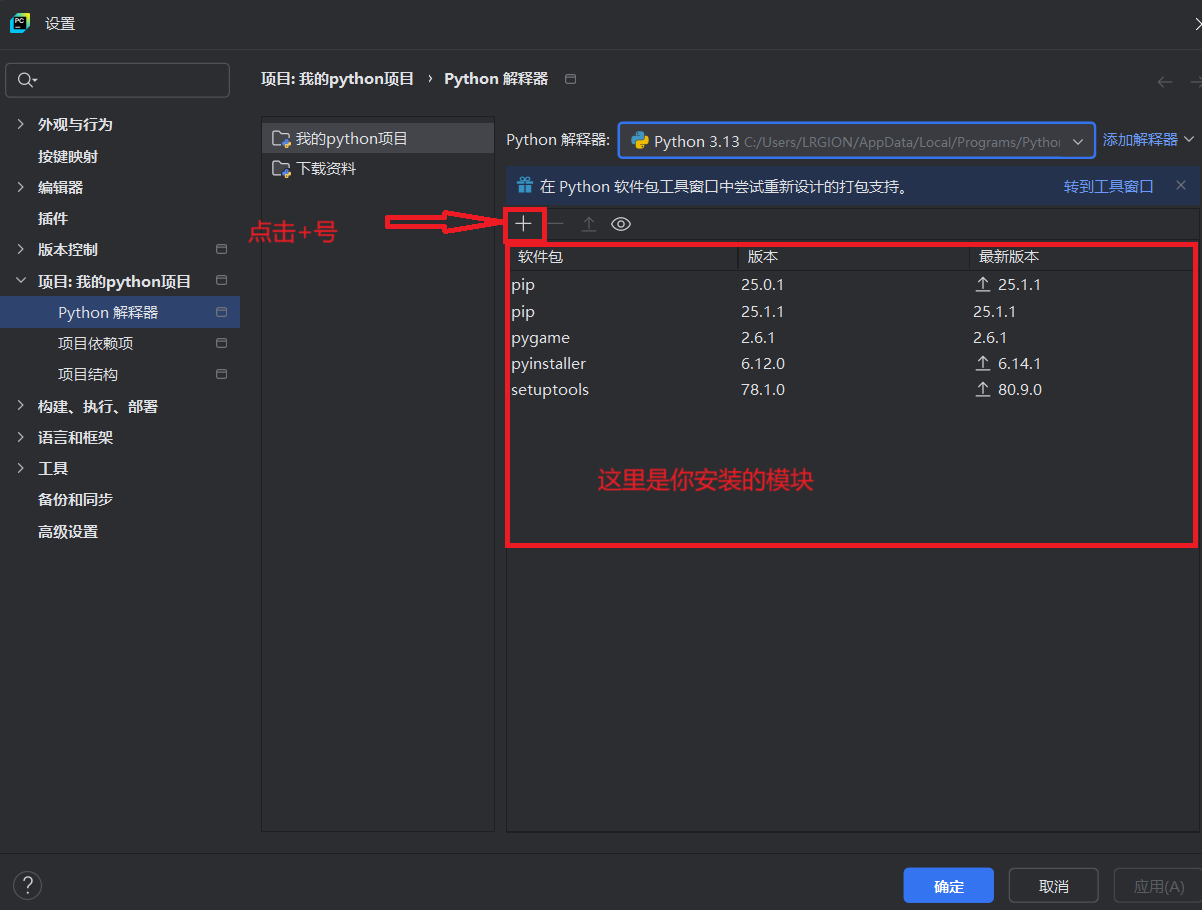
- pycharm里面直接下载
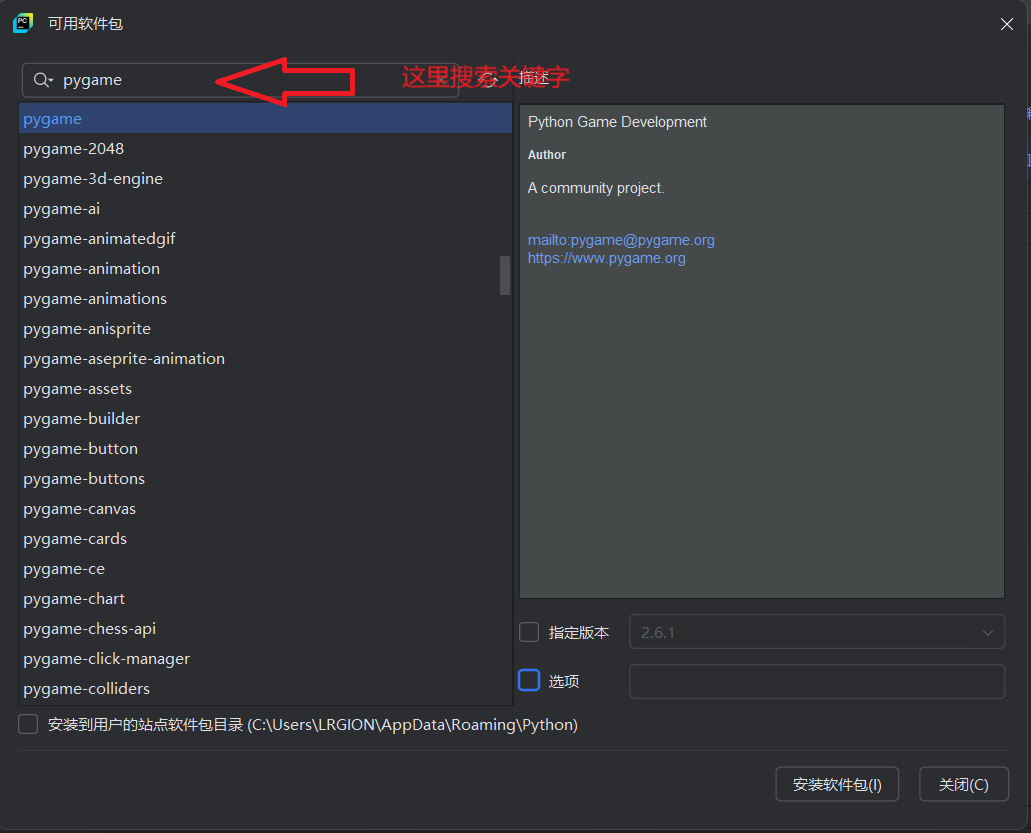
- 示例用
pygame写个简单程序 - 这里展示目的主要是展示模块下载后怎么使用。就是直接导入就完了,里面的方法需要参考该模块的说明使用,在pip官网有说明。
py
# 导入模块
import pygame
import sys
# 初始化pygame
pygame.init()
# 设置窗口尺寸
width, height = 800, 600
screen = pygame.display.set_mode((width, height))
pygame.display.set_caption("移动的球")
# 球的属性
ball_pos = [width // 2, height // 2]
ball_radius = 30
ball_speed = 5
ball_color = (255, 0, 0) # 红色
# 游戏主循环
clock = pygame.time.Clock()
running = True
while running:
# 事件处理
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
running = False
elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:
if event.key == pygame.K_SPACE:
# 重置球的位置
ball_pos = [width // 2, height // 2]
# 按键处理(持续按键)
keys = pygame.key.get_pressed()
if keys[pygame.K_LEFT] and ball_pos[0] > ball_radius:
ball_pos[0] -= ball_speed
if keys[pygame.K_RIGHT] and ball_pos[0] < width - ball_radius:
ball_pos[0] += ball_speed
if keys[pygame.K_UP] and ball_pos[1] > ball_radius:
ball_pos[1] -= ball_speed
if keys[pygame.K_DOWN] and ball_pos[1] < height - ball_radius:
ball_pos[1] += ball_speed
# 渲染
screen.fill((255, 255, 255)) # 白色背景
# 绘制球
pygame.draw.circle(screen, ball_color, ball_pos, ball_radius)
# 更新显示
pygame.display.flip()
# 控制帧率
clock.tick(60)
# 退出游戏
pygame.quit()
sys.exit()